Unit 3. Basic Client-Server Communications
3.3. FTP connections. FTP clients
In this section we are going to see how to connect to a FTP server using a Java application. So, we need to implement an FTP client for this purpose. To access a FTP server through Java we’ll use Apache’s FTPClient class which is included in Apache’s Commons Net library. To do this, we will have to create a Maven or Gradle project in order to add this library in the dependencies, or download the corresponding JAR and include it in our project.
3.3.1. Connection
The most simple way to connect to an existing FTP server through FTP protocol (you can connect to an FTP server through HTTP protocol also) is opening a connection like this:
1FTPClient ftp = new FTPClient();
2try {
3 // Important (before connecting)
4 ftp.setControlEncoding("UTF-8");
5 ftp.connect("172.16.208.128");
6 System.out.print(ftp.getReplyString());
7 // If the server is in another network...
8 ftp.enterLocalPassiveMode();
9
10 if(!FTPReply.isPositiveCompletion(ftp.getReplyCode())) {
11 ftp.disconnect();
12 System.err.println("Error connecting to FTP");
13 }
14} catch (IOException e) {
15} finally {
16 if (ftp.isConnected()) {
17 try {
18 ftp.disconnect();
19 } catch (IOException ioe) {}
20 }
21}As you can see, we open a connection specifying the server IP or domain name (localhost if it’s running on the same machine). Then we print the response from the server and check the reply code (indicating an error or success) using the class FTPReply to know if the connection was successful or not.
Importante
The FTP server can close a connection if it has been inactive for a period of time, so it’s not guaranteed the connection will still be open anytime.
3.3.2. File listing
To list the contents of a directory, first we’ll have to log in, and then we can use the listFiles() method that returns an array of FTPFile objects, representing each one of them a file (or subdirectory, or link) inside the directory:
1if(ftp.login("arturo", "arturo")) {
2 FTPFile[] files = ftp.listFiles();
3 for(FTPFile file: files) {
4 String type = file.isDirectory()?
5 "Directory":file.isSymbolicLink()?
6 "Link":"File";
7 System.out.println(type + " -> " + file.getName());
8 }
9}3.3.3. Uploading files
Before uploading a file to the server we must know if that file is in binary or text format and set the FTP default file type to be transferred previous to send it. This is accomplished with setFileType(int type) method. Valid values are FTP.ASCII_FILE_TYPE (default) or FTP.BINARY_FILE_TYPE (recommended if you don’t know the type of a file).
Other useful methods are changeWorkingDirectory(String pathname) that changes the current working directory in the FTP server and changeToParentDirectory() which changes to the parent directory.
1public static void uploadFile(boolean isText, String filePath,
2 String nameInServer) {
3 // This is a method we have created to open a connection
4 if(!connect()) {
5 System.err.println("Cannot upload file, error connecting!");
6 return;
7 }
8
9 try(FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(filePath)) {
10 ftp.setFileTransferMode(
11 isText?FTP.ASCII_FILE_TYPE:FTP.BINARY_FILE_TYPE);
12 if(!ftp.storeFile(nameInServer, in)) {
13 System.err.println("Error uploading file " + filePath +
14 " (" + ftp.getReplyString() + ")");
15 } else {
16 System.out.println("File " + filePath +
17 " uploaded with name " + nameInServer);
18 }
19 } catch (IOException e) {
20 System.err.println("Error uploading file " + filePath
21 + e.getMessage());
22 }
23}3.3.4. Downloading files
To download a file is a very similar process but using a FileOutputStream on the local filename and the method retrieveFile.
1public static void downloadFile(boolean isText, String nameInServer,
2 String nameLocal) {
3 if(!connect()) {
4 System.err.println("Cannot download file, error connecting!");
5 return;
6 }
7 try(FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(nameLocal)) {
8 ftp.setFileTransferMode(isText?
9 FTP.ASCII_FILE_TYPE:FTP.BINARY_FILE_TYPE);
10 if(!ftp.retrieveFile(nameInServer, out)) {
11 System.err.println("Error downloading file " + nameInServer +
12 " (" + ftp.getReplyString() + ")");
13 } else {
14 System.out.println("File " + nameInServer +
15 " downloaded with name " + nameLocal);
16 }
17 } catch (IOException e) {
18 System.err.println("Error downloading file " + nameInServer +
19 e.getMessage());
20 }
21}3.3.5. Other operations
There are other useful operations that can be done from the FTP client, such as:
rename(String from, String to): Changes a remote file’s name.deleteFile(String pathname): Deletes a remote file.removeDirectory(String pathname): Deletes a directory, only if it’s empty.makeDirectory(String pathname): Creates a new subdirectory.printWorkingDirectory(): Gets the name of the current working directory.listNames()Gets only the names of the list of files inside the current directory.
Exercise 6
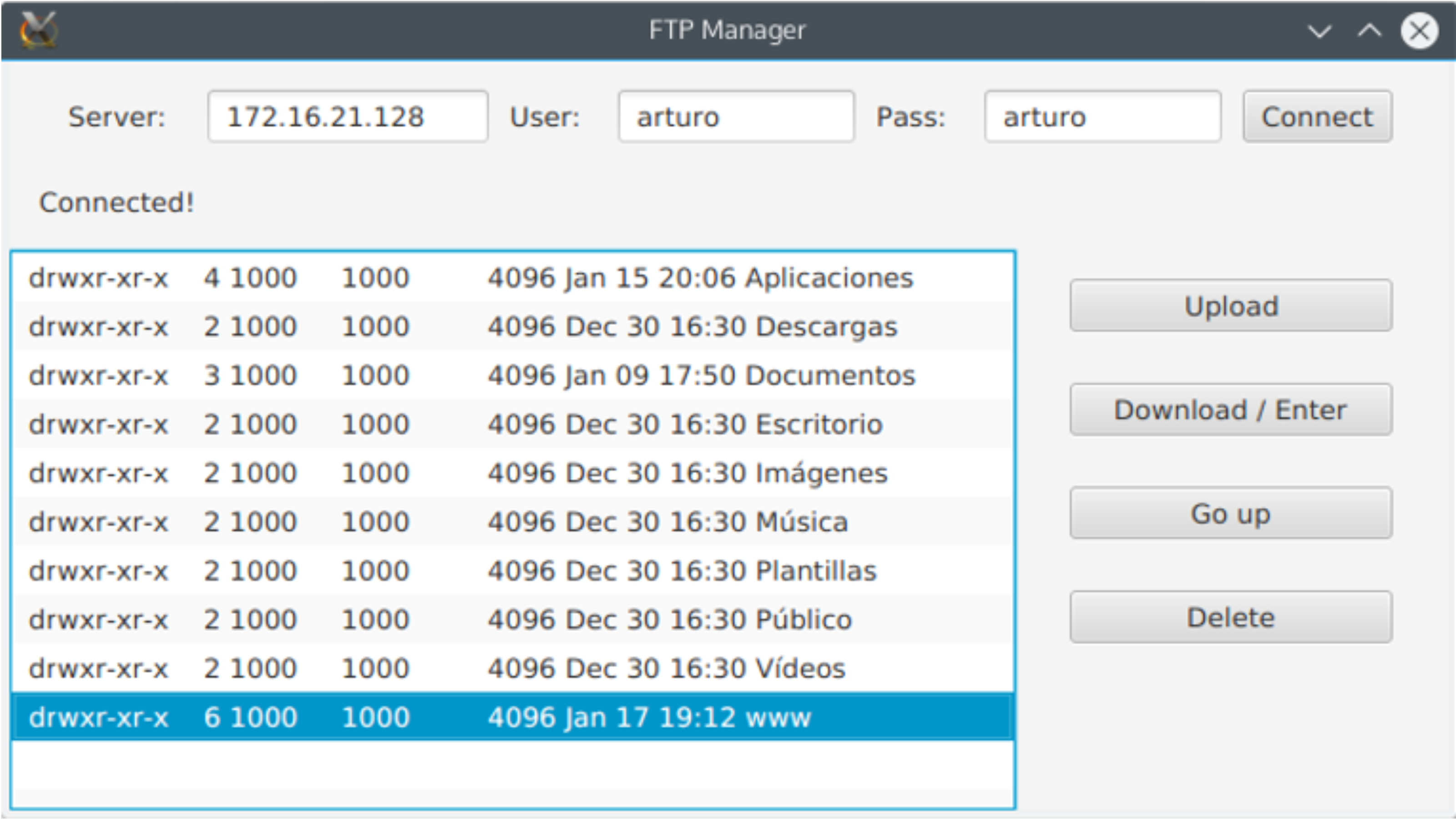
Create a JavaFX application called FTPManager. It will be a simple FTP client, which you’ll use to connect to a server (can be localhost or a virtual machine IP), list its contents on a ListView and do several actions. The application aspect should be more or less like this:
As you can see, once you enter a server address, a login name and password, and click the Connect button, the application will list the working directory contents. The other buttons will perform the following actions:
- Upload: Will open a
FileChooserdialog to select a file that will be uploaded to the FTP server (current directory). Dowload/Enter: Only active when something in the list is selected. Two situations can happen
- If the selected item is a directory, the application will change to that directory listing its files.
- If it’s a normal file, the application will open a
DirectoryChooserdialog to select a local directory and download the file there. Go up: Will change to the parent directory and list its contents. Delete: Only active when something in the list is selected. Will delete the file.There will be a label where you’ll show every action’s result, whether it’s a success or a failure. When it’s needed, refresh the list’s contents.
3.4. FTPS Connections (FTP Secure)
FTPS adds layers of security to standard FTP connections through the use of SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security). To access an FTPS server through Java, we will use Apache’s FTPSClient class from the Apache Commons Net library.
3.4.1. Connection
Connecting to an FTPS server is similar to connecting to an FTP server but using FTPSClient instead of FTPClient:
1ftps = new FTPSClient("TLS",false);
2try {
3 ftps.setControlEncoding("UTF-8");
4 //ftps.connect("54.38.240.72");
5 ftps.connect("ftp.marichelo.es");
6 ftps.login("maricheloftp", "marichelo");
7
8 if (!FTPReply.isPositiveCompletion(ftps.getReplyCode())) {
9 ftps.disconnect();
10 System.err.println("Error connecting to FTPS");
11 } else {
12 ftps.enterLocalPassiveMode();
13 ftps.execPROT("P");
14 System.out.println("Connected");
15 //testing chroot
16 System.out.println(ftps.printWorkingDirectory());//wich directory we are connected
17 ftps.cdup(); // cd.. trying to exit our home directory
18 System.out.println(ftps.printWorkingDirectory());
19
20 FTPFile[] files = ftps.listFiles(); //listing the files of the working directory
21 for(FTPFile file: files) {
22 String type = file.isDirectory()?
23 "Directory":file.isSymbolicLink()?
24 "Link":"File";
25 System.out.println(type + " -> " + file.getName());
26 }
27 }
28} catch (IOException e) {
29 e.printStackTrace();
30} finally {
31 if (ftps.isConnected()) {
32 try {
33 ftps.logout();
34 ftps.disconnect();
35 } catch (IOException ex) {
36 ex.printStackTrace();
37 }
38 }
39}Both uploading and downloading files are similar to FTPClient but using FTPSClient class instead.
3.5. SFTP Connections (SSH File Transfer Protocol)
SFTP is another protocol that provides a secure way to transfer files over an encrypted connection. To implement an SFTP client in Java, we can use the JSch library from com.jcraft.
3.5.1. Connection
Here’s a basic example of how to connect to an SFTP server using JSch:
1import com.jcraft.jsch.JSch;
2import com.jcraft.jsch.Session;
3
4JSch jsch = new JSch();
5try {
6 Session session = jsch.getSession("username", "yourserver.com", 22);
7 session.setPassword("password");
8
9 // Configuration to not validate the host key
10 session.setConfig("StrictHostKeyChecking", "no");
11
12 session.connect();
13
14 // Connection established
15 session.disconnect();
16} catch (Exception e) {
17 e.printStackTrace();
18}3.5.2. Listing Files, Uploading, and Downloading
For operations like listing files, uploading, and downloading, you’ll need to use the ChannelSftp class from JSch. Here’s a basic outline:
1import com.jcraft.jsch.Channel;
2import com.jcraft.jsch.ChannelSftp;
3import com.jcraft.jsch.JSch;
4import com.jcraft.jsch.Session;
5
6// Establish connection
7Channel channel = session.openChannel("sftp");
8channel.connect();
9ChannelSftp sftpChannel = (ChannelSftp) channel;
10
11// List files
12Vector<ChannelSftp.LsEntry> list = sftpChannel.ls("/path/to/directory");
13for (ChannelSftp.LsEntry entry : list) {
14 System.out.println(entry.getFilename());
15}
16
17// Upload file
18sftpChannel.put("localfilepath", "remotefilepath");
19
20// Download file
21sftpChannel.get("remotefilepath", "localfilepath");
22
23// Close connection
24sftpChannel.exit();
25session.disconnect();